Advantages Disadvantages Software Configuration Management
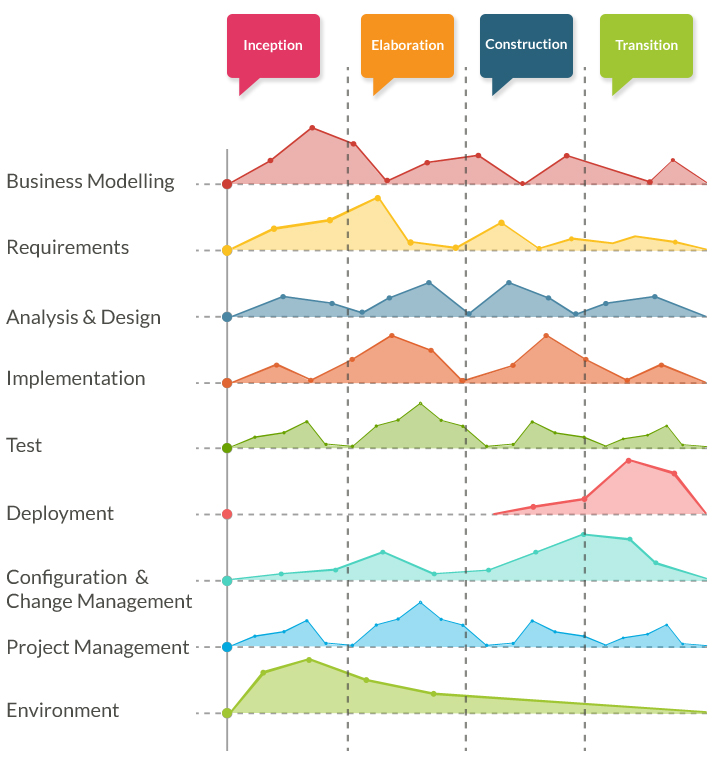
The first we heard about Agile development (or the term Agile) was back in 2001, when a community of developers that was tired of using development methods considered to be “heavy” – namely, the waterfall model – decided to set out a manifesto: The Agile Manifesto. This very important document had so much impact that it has worked as a bible for Agile development even until today, laying out all principles and good practices. Agile methodologies argue that, above all, we should seek client satisfaction through continuous deliveries of value-adding software, by keeping up constant communication with the client and, also, by focusing on communication between team members. Contrary to previous practices, the Agile methodology is not characterised by the complete definition of a product – a complete analysis or the definition of all categories/requirements – but by a dynamic interaction that allows constant delivery. According to the Agile Manifesto and some of its 12 principles: • Customer satisfaction is the priority, demonstrated through continuous deliveries and added value. • Changes to the requirements should be accepted, even if at a late stage of the development: “Agile processes harness change for the customer’s competitive advantage”, as is stated in the Manifesto.
There are many advantages and disadvantages for implementing CMMI-DEV in a Software Development IT Organization. Advantages of CMMI. There are numerous benefits of implementing CMMI in an IT / Software Development Organization, some of these benefits are listed below.
• The customer and the development team should work together on a daily basis. • It is necessary to provide a good environment and good support to development teams. Only in this way it is possible to keep them motivated. • Agile processes promote sustainable development because of their constant rhythm and technical excellence, which improves productivity. • Retrospective moments inside a team are essential, allowing it to make the necessary adjustments and promote efficiency.  Basically, Agile development follows an incremental model, which develops collaboration within the team and continuous planning, as well as everlasting evolution and learning. Agile methodologies should respect the software development cycle – planning, execution and final delivery – therefore allowing software to be developed in stages; this makes it easier to identify and resolve bugs.
Basically, Agile development follows an incremental model, which develops collaboration within the team and continuous planning, as well as everlasting evolution and learning. Agile methodologies should respect the software development cycle – planning, execution and final delivery – therefore allowing software to be developed in stages; this makes it easier to identify and resolve bugs.
The main advantage of using Agile methodologies is not only the fast delivery of software, but also the constant delivery of value to the customer, since deliveries are incremental. There are countless methodologies that follow this Agile mindset. In this blog post, we highlight the five main Agile methodologies and their advantages and disadvantages in the software development universe. Main Agile methodologies: 1. Scrum is, undoubtedly, the most used of the many frameworks of the Agile methodology. Scrum is characterised by cycles or stages of development, known as sprints, and by the maximisation of development time for a software product. How to use cakewalk dimension pro. It is usually used in the management of development projects for software products, but it can also be used in a business-related context.
Every day there are small 15-minute meetings, the daily scrum, that take the role of synchronising activities and finding the best way to plan the workday. Advantages: Disadvantages: • There is a lot of motivation in teams, because programmers want to meet the deadline of every sprint; • The transparency allows for the project to be followed by all members of a team or even an organisation; • The focus on quality is a constant in the scrum method, resulting in fewer mistakes. • The dynamics of this method allow developers to reorganise priorities, ensuring that sprints that have not yet been completed get more attention • The segmentation of the project and the search for agility of the development can sometimes lead the team to lose track of the project as a whole, focusing only on one part; • Each developer’s role may not be well defined, resulting in some confusion amongst team members.